In an industrial world where the reality of plant maintenance is, for many, still defined by 19th century resources like shop rags (versus plentifully available high-tech industrial wipers), it may seem strange to discuss seemingly futuristic innovations such as Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR & VR). But new research from global management consultancy PwC points out that the “future” is happening right now in manufacturing, and that to stay competitive, manufacturers need to start taking advantage of the productivity, safety, and quality control benefits AR & VR provide.
 Get the complete infographic (PDF)
Get the complete infographic (PDF)
The new reality in manufacturing
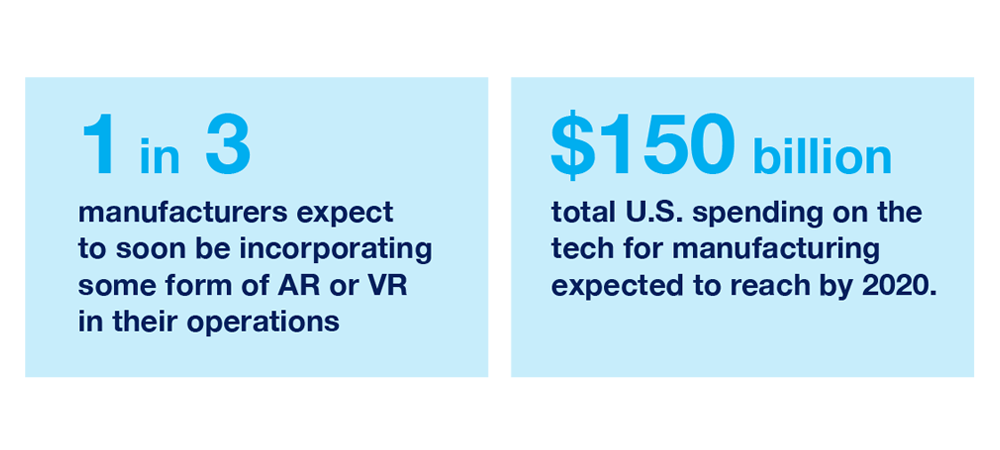
According to the study, one third of manufacturers expect to soon be incorporating some form of AR or VR in their operations, with total U.S. spending on the tech for manufacturing expected to reach $150 billion by 2020. An equal number, however, still consider the technology “not ready for prime time.” The doubters notwithstanding, such a heavy level of investment qualifies this as a turning point – and those who make the turn now stand to enjoy considerable advantages.
Consider the four key areas in which AR & VR are already having a transformative impact: plant maintenance, design and development, safety and training, and data access and management.
Plant maintenance enters the twenty-first century
As mentioned above, innovators have for some time been upgrading essentials of cleaning and maintenance, replacing those outdated rags with efficiency- and effectiveness-enhancing wipers.
Now innovation is making a quantum leap. As just one example, consider how AR-enabled glasses are equipping workers to see and hear step-by-step instructions on how to fix machinery, without ever pausing to find and flip through a manual, or struggle to interpret directions. The result is increased speed, accuracy and overall maintenance productivity, not to mention reduced downtime. Small wonder, then, that 20% of manufacturers point to maintenance as one of their primary, early applications of the new tech.
The big trend in product design and development
Perhaps the best-known manufacturing application of AR/VR technology is actually a “pre-manufacturing” use, in the product design, and development phase. Thirty-nine percent of companies surveyed said that they are now taking a virtual approach to new product development, as it allows them to more quickly work through design iterations, reducing the need for physical models, and allowing collaborative input from customers, all before any “real” (and expensive) prototyping or production begins.
Once it does begin, the new technology can also improve assembly, particularly in complicated processes. Workers wearing smartglasses can monitor complex assemblies, confirming proper assembly sequence, and making real-time adjustments (often without any downtime), all the while automatically tracking and downloading assembly information into management databases.
 Get the complete infographic (PDF)
Get the complete infographic (PDF)
Taking safety and skills training to the next level
Some 28% of manufacturers use AR and VR to enhance safety and training. This may be fairly straightforward, as in updating hardhats to smarthats, equipping protective headgear with sensors to monitor both the worker’s physical well-being and the external conditions around her or him. Or it can change things from the ground up, as when manufacturers use digital avatars – representing factory workers – to test how changes to the factory floor could minimize wasted motion and reduce strain on employees’ bodies during the assembly process.
As more and more companies look to retrain their workforces to effectively manage an increasingly tech-driven workplace, VR headsets will support, or in some cases replace, human instructors, allowing companies to more quickly, efficiently, and thoroughly train new employees or update existing workers on those seemingly endless system upgrades. The technology allows trainees to get “hands-on” experience without ever actually laying their hands-on equipment – freeing up the real equipment to stay in use, further reducing downtime.
Getting real with data in manufacturing
Manufacturing data is only an asset if it’s accurate, current, and accessible. Thankfully, the increased use of AR and VR will help improve all three factors. Twenty percent of manufacturers currently employ AR and VR specifically for data-related benefits, but that percentage is bound to quickly rise.
Accuracy is improved by the constant interaction of human workers with the data they need. For instance, an AR maintenance module that incorrectly instructs a worker in a process is subject to the observation of a real, live human, who can employ the “non-artificial” intelligence of common sense to see, note, and report that what looked good in algorithmic theory doesn’t quite play out in practice. Because that reporting can be in real-time, through the AR interface, changes can be made quickly, avoiding replication of problems and keeping the data current. And as both wearable AR glass devices and VR headsets can be connected to your entire data ecosystem, workers can immediately access the information they need for training, repairs or maintenance, as well as report and correct issues in real time.
It’s time
If you’re part of that third of all manufacturers who still think that AR and VR technologies are more suited for shopping malls than the shop floor, it’s time to reconsider just how the latest trends in Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality can keep you competitive – and even a step ahead.
Get the complete infographic (PDF)
Sources
PwC research report: For U.S. manufacturing, virtual reality is real
IoT for all: AR is becoming a focus in maintenance technology
